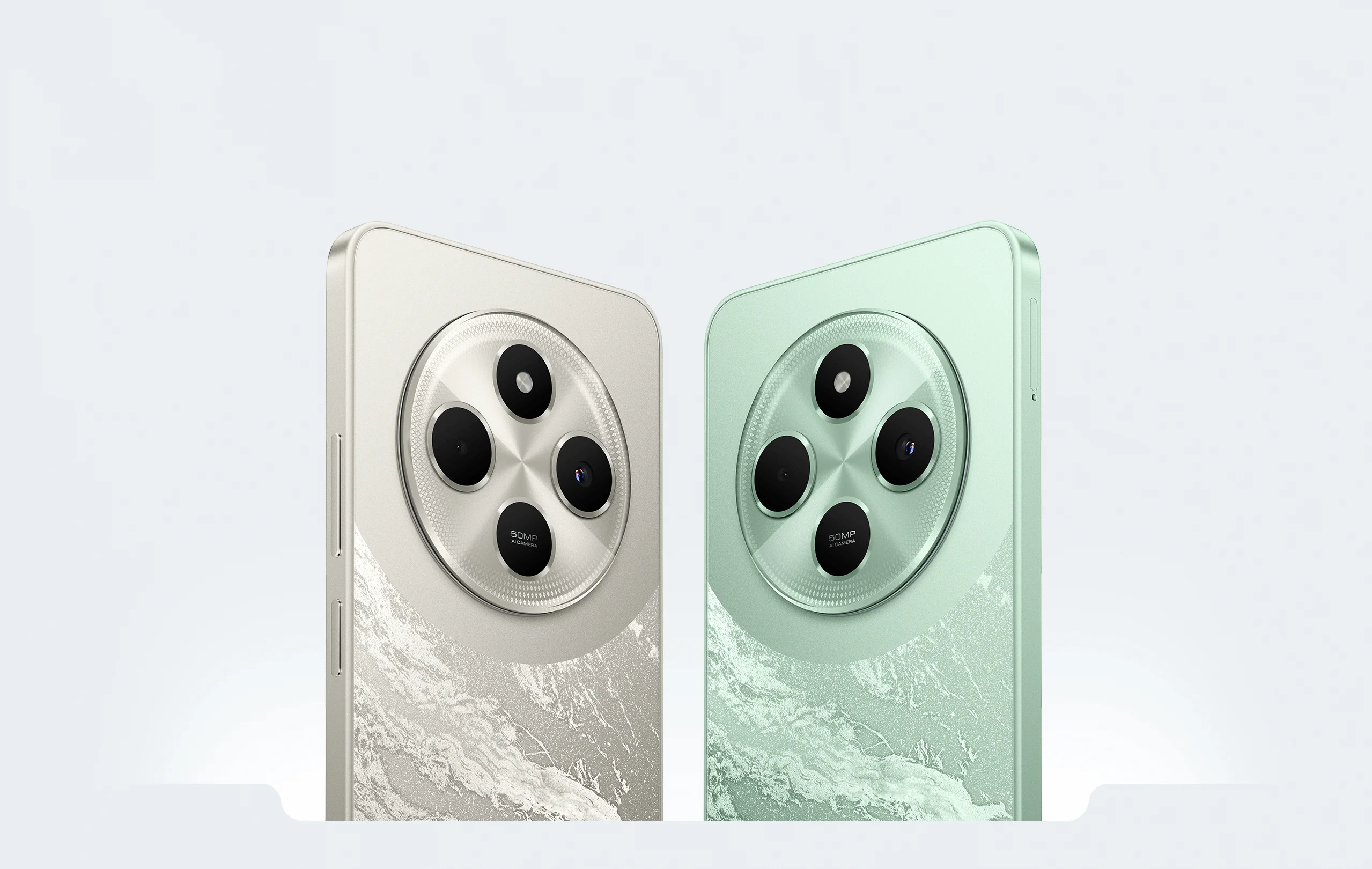
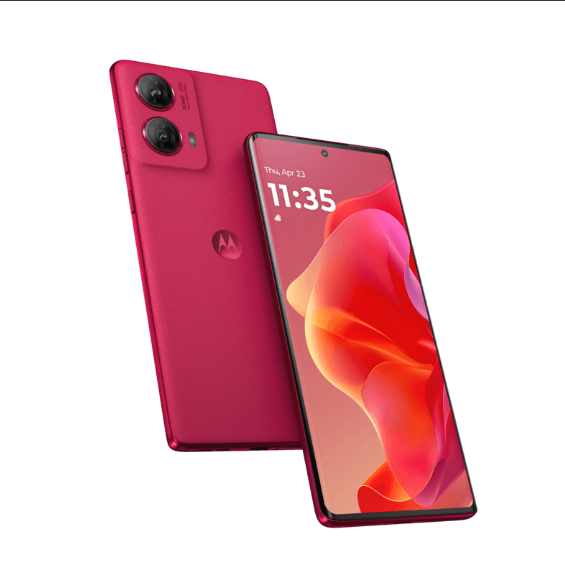
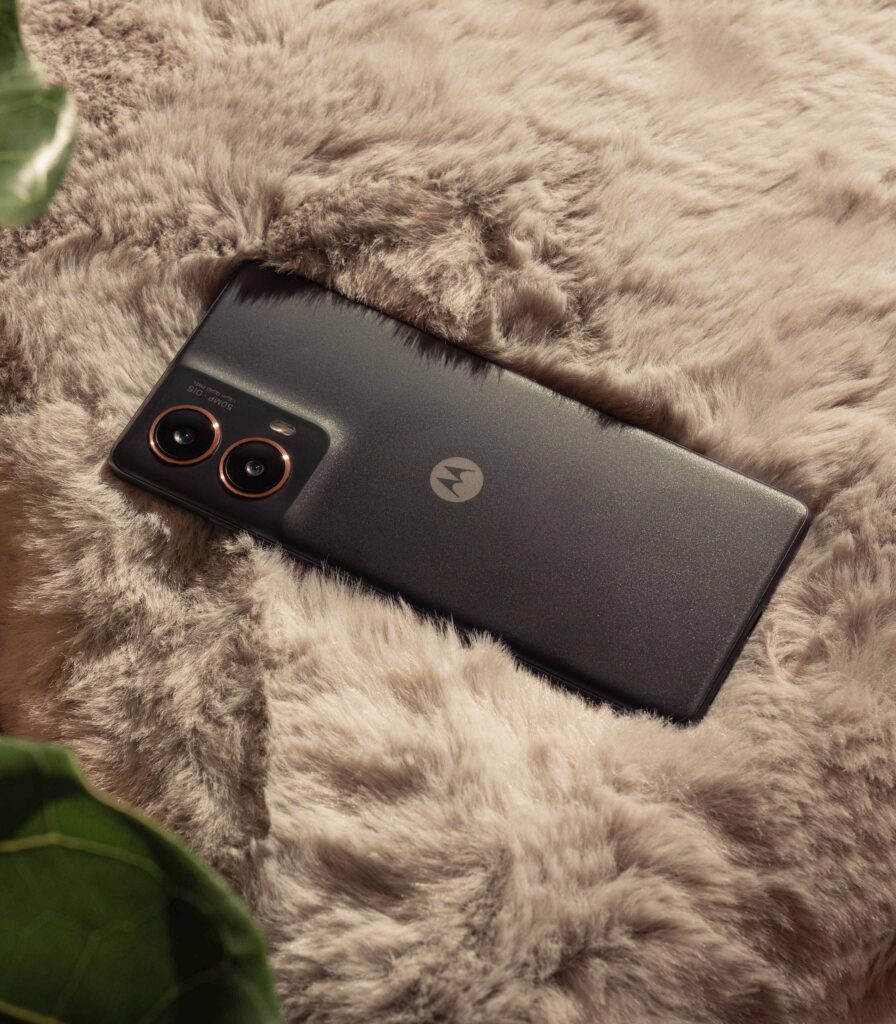
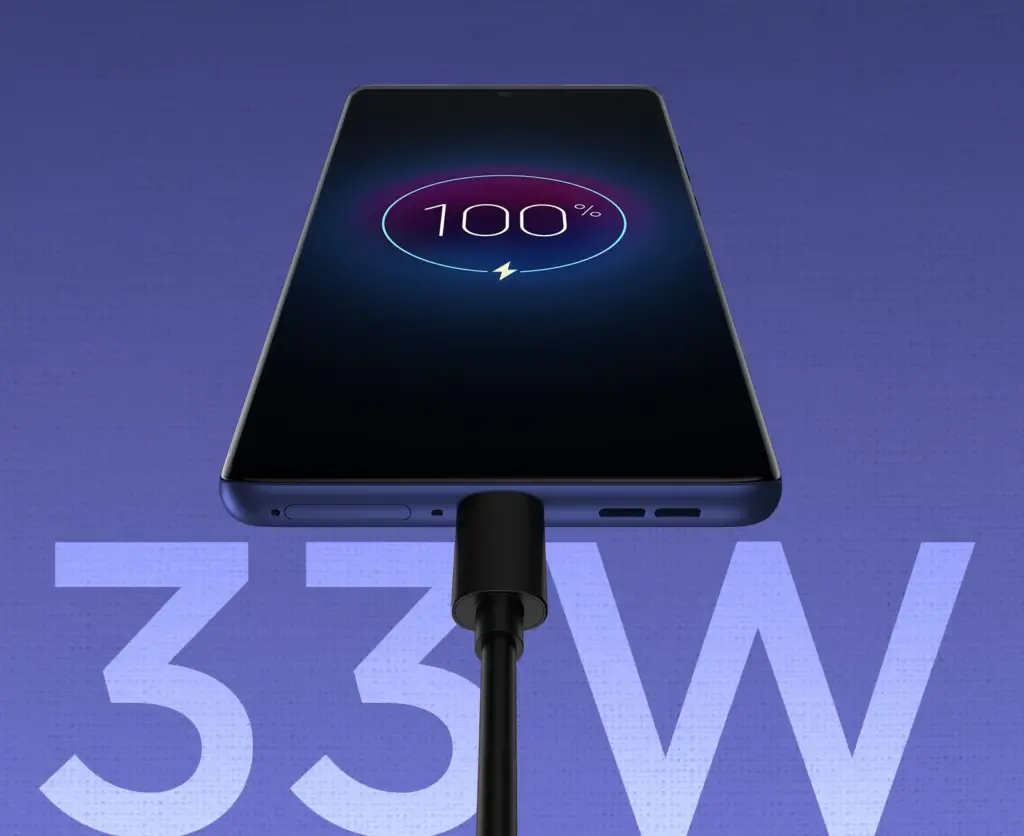
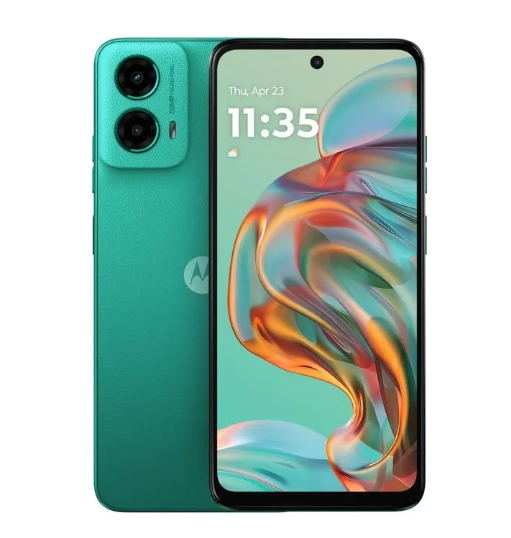
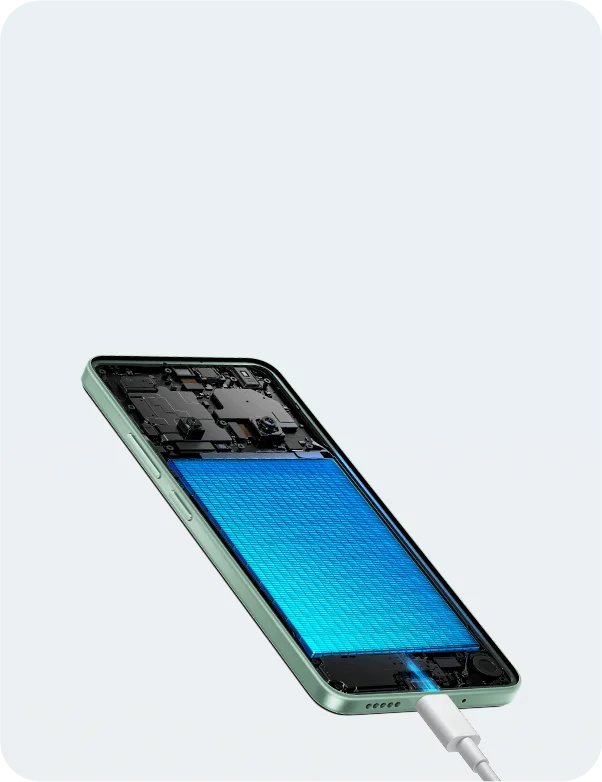
Nothing Phone (2a) 5G एक नया स्मार्टफोन है जो अपनी प्रीमियम सुविधाओं और अनोखा डिज़ाइन के साथ मार्केट में आया है। इस फोन में वह सब कुछ है जो एक यूज़र को चाहिए, चाहे वह बेहतरीन कैमरा हो, शानदार डिस्प्ले, या फिर लंबी बैटरी लाइफ। आइए जानते हैं इस स्मार्टफोन के बारे में विस्तार से।

Specifications Table
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| RAM | 12 GB |
| Storage | 256 GB |
| Display Size | 17.02 cm (6.7 inch) |
| Display Type | Flexible AMOLED |
| Display Resolution | 2412 x 1084 Pixels (Full HD+) |
| Processor | MediaTek Dimensity 7200 Pro |
| Rear Camera | 50 MP + 50 MP (OIS) |
| Front Camera | 32 MP |
| Battery | 5000 mAh |
| Operating System | Android 14 with Nothing OS 2.5 |
Camera: Make every Moment Special
Nothing Phone (2a) 5G के कैमरे में वो सब कुछ है जो आपको एक बेहतरीन फोटोग्राफी अनुभव देने के लिए जरूरी है। इसमें 50 MP का मुख्य कैमरा है, जो OIS (Optical Image Stabilization) के साथ आता है। इससे आपको कम रोशनी में भी स्पष्ट और स्पष्ट तस्वीरें मिलती हैं। साथ ही, 50 MP का Ultra Wide कैमरा है जो 114° का फील्ड-ऑफ़-व्यू प्रदान करता है, जिससे आप बड़ी घटनाओं और समूह फ़ोटो को आसानी से कैप्चर कर सकते हैं।

इसके अलावा, इस फोन में 32 MP का फ्रंट कैमरा भी है, जो आपके सेल्फ़ी के अनुभव को और भी बेहतर बनाता है। यह कैमरा 1080p पर 60 FPS की वीडियो रिकॉर्डिंग का समर्थन करता है, ताकि आप अपनी खूबसूरत यादों को एक शानदार तरीके से रिकॉर्ड कर सकें।
Also check: POCO C75 5G:Ultimate Powerful, Performance, and Style in Your Hands
Display: Stunning Visual Experience
Nothing Phone (2a) 5G का डिस्प्ले भी कमाल का है। इसमें 17.02 cm (6.7 inch) का फ्लेक्सिबल AMOLED डिस्प्ले है, जो 1.07 बिलियन रंगों को प्रदर्शित करने की क्षमता रखता है। इसका रेजोल्यूशन 2412 x 1084 पिक्सल्स है, जो Full HD+ डिस्प्ले के रूप में उच्च गुणवत्ता वाले दृश्य अनुभव प्रदान करता है। इसकी ब्राइटनेस 700 निट्स तक है और पीक ब्राइटनेस 1300 निट्स तक पहुँच जाती है, जिससे आपको बाहर की धूप में भी साफ और स्पष्ट स्क्रीन दिखाई देती है।
इसमें 120 Hz का रिफ्रेश रेट है जो आपके सभी इंटरएक्शन को स्मूथ और शानदार बनाता है। इसके अलावा, इस स्मार्टफोन के 2.1 mm के बेहद पतले बेज़ल्स के साथ स्क्रीन-टू-बॉडी रेशियो 91.65% तक है, जो आपके डिस्प्ले अनुभव को और भी अधिक रोमांचक बनाता है।

Nothing OS 2.5 and Android 14
Nothing Phone (2a) 5G में Android 14 का सपोर्ट है और इसमें Nothing OS 2.5 यूज़र इंटरफ़ेस है। यह ऑपरेटिंग सिस्टम आपको तेज़ और स्मूथ अनुभव प्रदान करता है। Nothing OS का डिवाइस यूज़र इंटरफेस कस्टमाइजेशन और उपयोगिता को ध्यान में रखकर बनाया गया है, जिससे आप बिना किसी परेशानी के अपने पसंदीदा फीचर्स का इस्तेमाल कर सकते हैं।
साथ ही, Nothing OS में नई विगेट्स की सुविधा भी है, जो आपको होम और लॉक स्क्रीन से ही अपने ऐप्स और अक्सर इस्तेमाल होने वाली सुविधाओं तक पहुंचने की अनुमति देती हैं। इन विगेट्स के जरिए आप अधिक जानकारी देख सकते हैं, जैसे कि आपके ऐप्स का हाल और अन्य महत्वपूर्ण डेटा।

Glyph Interface: Interaction without a Screen
Nothing Phone (2a) 5G में एक अनोखा Glyph Interface का फीचर है, जो स्क्रीन के बिना ही सूचना प्राप्त करने का एक तरीका प्रदान करता है। जब आप अपना फोन नीचे रखते हैं, तो यह आपको महत्वपूर्ण सूचनाओं से अपडेट रखता है। Glyph Interface अब नई त्रिकोण लाइट कंफिगरेशन और 15 इनोवेटिव फ़ंक्शन्स के साथ आता है। यह न केवल कॉल और नोटिफिकेशंस को दर्शाता है, बल्कि वॉल्यूम इंडिकेटर, टाइमर और काउंटडाउन के रूप में भी काम करता है। इसके जरिए आप थर्ड-पार्टी ऐप्स के साथ काम करके अपनी डिलीवरी ट्रैकिंग और अन्य सुविधाओं को आसानी से देख सकते हैं।
Battery and Processor
Nothing Phone (2a) 5G में 5000 mAh की बैटरी दी गई है, जो आपको लंबी बैटरी लाइफ प्रदान करती है। इसका प्रोसेसर MediaTek Dimensity 7200 Pro है, जो एक ऑक्टा-कोर प्रोसेसर है और उच्चतम प्रदर्शन सुनिश्चित करता है। इस प्रोसेसर की मदद से आप अपने गेम्स और मल्टीटास्किंग को आसानी से संभाल सकते हैं, बिना किसी लैग या हिचकी के।

Conclusion
Nothing Phone (2a) 5G एक शानदार स्मार्टफोन है जो बेहतरीन कैमरा, अद्भुत डिस्प्ले, और शक्तिशाली प्रोसेसर के साथ आता है। इसकी सुविधाएँ इसे एक प्रीमियम स्मार्टफोन बनाती हैं, और इसकी Glyph Interface और Nothing OS के कारण यह और भी आकर्षक बन जाता है। यदि आप एक स्मार्टफोन चाहते हैं जो न केवल दिखने में शानदार हो, बल्कि प्रदर्शन में भी बेहतरीन हो, तो Nothing Phone (2a) 5G आपके लिए एक बेहतरीन विकल्प हो सकता है।